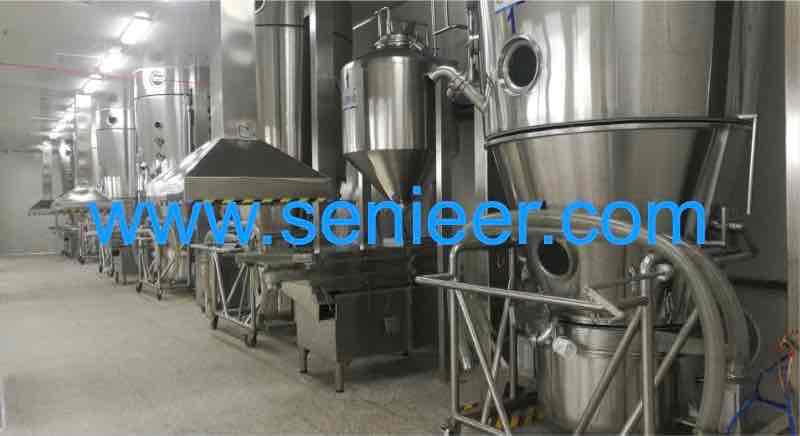

Are you wondering, How does a Fluidized Bed Dryer work? and what is the application of fluidized bed dryer Today, I’ll take you through:
Fluidized bed dryer parts
Fluid bed dryer (fluidized bed dryer) diagram
Fluid bed dryer (fluidized bed dryer) process
Fluid bed dryer animation
Application of Fluid bed Dryer
Fluidized bed dryer advantages and disadvantages
And more!
You can also visit our Fluid bed dryer product Page here where you can request a quote and also read about fluid bed processors.
Drying is a key unit process in the chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries. It requires heating making it capital and energy-intensive. Drying may make up 60-70% of the total production cost.
Fluid bed dryers have been widely adopted for drying granules and powders in solid dosage drug manufacture. Senieer produces very high-quality bed dryers at competitive factory prices.
For better understanding, let’s examine each term in the phrase “Fluidized bed dryer.”
In short: In a fluid bed dryer, the inlet air stream is blown past solid powder molecules at rest. The particles are taken up in the dry & hot air stream and dehydrated through evaporation. Read on for the full explanation of the fluidized bed drying process.
You’ll find the fluid bed dryer in pharmaceutical industries and application of fluidized bed dryer are humongous. Its main role includes drying granules produced by the wet granulation process. If you’re not familiar with this process, it simply involves agglomerating small powder particles together by using a granulating liquid solution.
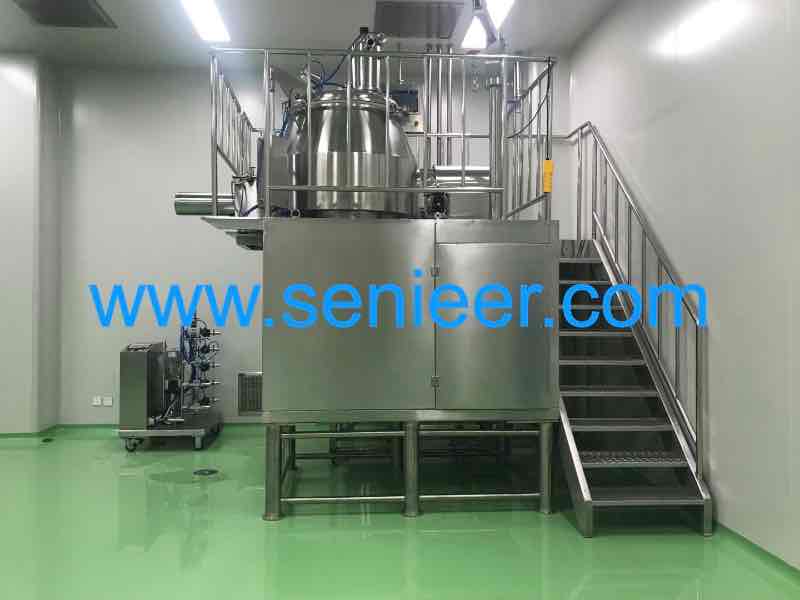

Part of the granulation solution includes a volatile solvent. We can eliminate this solvent by evaporating it in the dryer.
Applications of the fluidized bed dryer equipment include:
Food industries: Food processing, dehydration, and preservation such as drying chips
Fertilizer industry: Drying of inorganic fertilizers such as calcium fertilizers
Continuous fluid bed drying means materials are flowing into the equipment, getting dried and discharged all without interrupting the process.
And what do we mean by “batch drying?”
Batch drying implies that a fixed amount of material is fed into the dryer in one go. Drying is then carried out and when the endpoint is reached, the materials are discharged. You can also say that drying is done in sets or groups.
While continuous drying may have higher output rates, the pharmaceutical industry still relies on batch fluidized bed dryers (fluidized bed dryer).
Why are batch fluidized bed dryers still used?
In this chapter, you learned about the basics of the fluidized bed dryer (fluidized bed dryer). Next, I’ll take you through the main parts of this drying equipment.
For a good understanding of the fluid bed dyer’s working principle, you must know its parts. There are three systems, really:
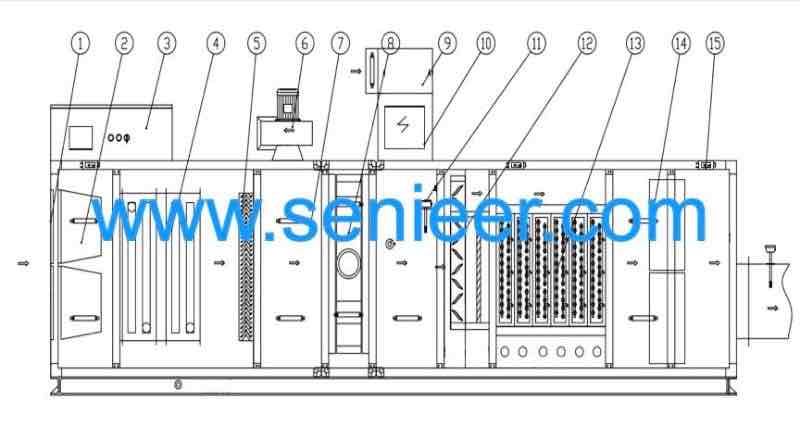
For instance, the main tower consists of the bowl, product container, bag filters, etc. You’ll learn about the function of each system along with its main components.
Function: “Supplying fresh, filtered, and heated air required for fluidizing & drying solid particles.”
The AHU resembles a rectangular container. One end serves as the fresh air inlet. The other extends in a vent that links the AHU to the fluid bed dryer. Some components of the fluid bed dryer’s AHU include:
The first filter medium is the G4 class filter. Its specification means it can remove airborne particles of 10μm.
You can see such particles with your naked eye. For instance, flower pollen. Senieer’s offers washable G4 filters that will save your costs.
It’s the second filter mounted just after the primary filter. It deals with very fine dust and may remove particles as small as 1μm.
There are usually two types of dehumidifiers:
First, the surface cooling dehumidification condenser coil. And second the wheel dehumidification unit. Now depending on the humidity of the air, they may be optional.
I’ll briefly explain how the wheel dehumidification unit works as the condenser coil is relatively easy to understand.
It’s also called the “Desiccant dehumidification wheel.” It consists of a wheel made up of corrugated material. The material on the wheel is a desiccant that attracts and retains water from the air.
You need the desiccant wheel when dealing with air with low humidity levels. Silica gel is an example of a desiccant material used in the wheel.
Some AHU units have two dehumidifiers: The condenser coils are positioned before the wheel dehumidification unit.
It draws air from the surroundings inside the AHU unit past the filters and into the heating chamber.
The next process after filtering and dehumidifying is heating. Cool incoming air absorbs heat from the surface of heated pipes. Now you may heat the pipes via steam or electricity. Our AHU comes with electric heating coils, but we also offer steam heating as an optional feature.
Before the hot air leaves the UHA unit, it undergoes final filtering. For this, we use a high-efficiency HEPA filter. It can remove very small particles as small as 0.3 μm in diameter.
How is this possible?
The mechanical filter contains fibers arranged randomly forming a dense mat. And so you get an idea of what can be filtered: it removes tobacco smoke, bacteria, pigments, spores, etc.
The airstream coming into contact with the drug granules must be very clean and free from bacteria that’s why we need three filtering steps.
Other key components of the AHU include the sensors, differential pressure meter, control panel, etc.
Here are its main parts:
The base part connects to the AHU unit via a stainless steel tube ferrying the clean, hot & dry air. A butterfly valve along the air inlet tube stops the air intake when closed.
The base part also consists of the inlet air plenum. The plenum chamber facilitates the transfer of the air up the main tower.
Before production starts, the product chamber and the bottom chamber are interlocked. An inflatable gasket seal ensures the connection is airtight and leak-proof.
Next, let’s look at the product container.
As the name dictates, this container holds wet material that needs drying. It’s usually wet granules produced by the high shear mixer.
The product container comes with its movable trolley. Sometimes it’s detached from the fluidized bed dryer and wheeled to the next process equipment such as the lifting column.
Another important feature of the product container is the bottom mesh/distributor plate. It’s held in place using SS clamps.
Just a mesh/metal screen with perforated holes. Its function is to resist airflow coming from the bottom chamber. Doing so, it evenly distributes air around the product container. The mesh also holds the product.
Other main features of the product container include:
– Viewing glass port (provides the operator with visual feedback)
– Sampling port (allows easy collection of samples from the product container)
– Product temperature sensor (Optional in some fluid bed dryers, but important for monitoring product temperatures)
It’s the area just above the product container. The connection between it and the product chamber is also made airtight with an inflatable gasket.
It’s the place in which fluidization takes place as air is drawn into the main tower past the bottom bowl and product chamber.
The expansion chamber forms the middle part of the tower. It’s integrated with the filter housing chamber that holds the double structure filter bag. Filter bags resemble sacks suspended over the process chamber.
Air flows upwards during fluidization and may carry in it small particles known as fines. The filter bags prevent fines from being exhausted.
The filtering bags become clogged with particles and require mechanical shaking to dislodge this dust layer. Shaking is done by pneumatic cylinders mounted at the top of the main tower.
Two cylindrical pipes emerge from the expansion of the fluidized bed dryer from each side of the filter bags. They subsequently form into one vent that’s connected to the blower. They are fitted with dampers with actuators. The actuator is a device that moves the damper allowing the closure and opening of the vents; first, it must receive an electrical signal from the control system.
Some fluidized bed dryers have a second filter unit. It captures fines that have passed through the filter bag system.
When used, it provides a higher filtering degree. Hence, more protection of the environment by reducing particulates in the exhaust gas. It’s also good when dealing with harmful substances needing the highest degree of containment.
In our fluid bed dryer, we use a centrifugal type blower. Its main parts include the impellers, driveshaft, drive mechanism (motor), casing, and inlet & outlet ducts.
During operation, the impeller rotates, which also causes the air molecules to rotate. The impeller also impacts centrifugal force on the air molecules causing them to move radially out.
On the outlet side, the air gains positive pressure and kinetic energy as it’s expelled. Inside the blower, the displacement of air creates negative pressure. So more airflows into the blower. Centrifugal pumps are thus ideal for drawing air through resistance such as dampers, filter bags, etc.
Our blower comes with a dynamically balanced impeller. The blades are curved backward meaning they face away from the direction of the airflow. The fluidized bed dryer industrial blower also has an all-steel construction with anti-vibration mounting to make it quieter.

From the control panel, the operator can control the inlet temperature, set the filter bag shaking time, start & stop the blower motor, lift & lower the product chamber, read the exhaust temperature, and more.
Opting for a PLC automated control system makes controlling the drying process more efficient. Senieer’s fluid bed dryers also adopt Siemen’s intelligent touch input panel for better human-machine interfacing.
Other parts include the explosion vent/port that extends from the expansion chamber. It has a rapture disk tested at a pressure of 2 Bar(as optional item).
Earthing device: Prevents the danger of static electric electricity by absorbing and grounding the static charges.
In this chapter, you’ll discover exactly how the fluidized bed dryer works. We’ll also go over the factors influencing the drying rate.
AHU preconditioning takes place along with warming up the main tower. Similarly, compression air inspections should be done to ensure that joints formed by inflation gaskets are leak proof.
Loading of materials involves adding a fresh batch of wet granules into the product chamber. Through negative pressure feeding, materials can be sucked from the high shear mixer chamber through a feeding tube.
Switching the blower unit on is done from the control panel. Once the blower is operational, the air is drawn continuously from the AHU unit and into the tower through the lower plenum.
Inlet air is blown up through the static powder bed. As the velocity of the air increases so does the space between powder particles until the particles become suspended in a bed. The fluidization process is thought to occur in five stages including smooth fluidization, bubbling fluidization, turbulent fluidization, and fast fluidization.
The drying process takes place in 3 stages until the endpoint is reached. (At the end-point the solid particle’s moisture level is equal or less than 1%):
Wet particles are suspended in the hot and dry air stream. Moisture on the particles’ surface evaporates as heat flows through the body (conventional heating). The rate of drying slowly increases as the particles absorb more heat.
The moisture lost during preheating is still small. But the temperature of the bed rises steadily.
Why is it called the constant rate?
The rate of drying remains constant as a function of time. In studies, plotting the amount of moisture lost against time gives a linear graph. In the preheating stage, the bed’s temperature was rising. But in this stage, the particles remain at the same temperature.
It’s the case because any energy supplied is taken up by the evaporating molecules as they transition from the liquid to the gaseous state.
Most of the moisture is lost in this stage.
Particles have lost most of their moisture and are nearing the drying end-point. With the surface moisture reduced, any remaining moisture is drawn from the porous core through capillary action.
Reduction in evaporation also causes the temperature of the bed to rise. Drying is stopped when the moisture level falls to less than 1%.
The blower continuously draws and excels air from the fluidized bed dryer. The airstream may contain very small particles called fines.
If they make it past the filter bags, they will be expelled into the surroundings. The filter bags capture the fines in their pores. But this causes the formation of a dust layer that clogs the filter bags causing a pressure drop.
Mechanical shaking is the best way to remove the dust layer, and it’s done by the pneumatic cylinders at the set intervals.
And since we have two filtering chambers, the shaking is alternated between the two.
Air exhausted from the fluidized bed dryer may go through a second filtering stage. This might help remove any particles that made it past the filter bag system.
Discharging refers to the removal of dried materials from the fluidized bed dryer. It can be done manually by unlocking and wheeling the product container on its trolley to the next process equipment.
Alternatively, vacuum conveying can be carried out by connecting the product container with a tube and creating negative pressure for suction using a vacuum transfer system.
After drying, the next process is milling carried out in the conical mill or comill.
The rate of drying depends on several factors including the product’s characteristics, process parameters, and even the design of a fluid bed dryer (fluidized bed dryer). For instance:
It has a direct bearing on the airflow pattern inside the fluid bed dryer.
The shape of the tower has also been shown to impact the drying rate with an annular shape preferred.
Increasing the inlet air temperature also increases the rate of heat and mass transfer. Both of which increase the rate of drying. But it’s not always possible to use high operating temperatures, especially for heat-sensitive materials. For instance, when drying Ibuprofen the temperature must not exceed 60 o C. In a study, where the researchers increased the operating temperature from 60 to 80 o C, there was a small increase in the drying rate. Though this was offset by the reduction in the energy efficiency of the fluidized bed dryer. So it’s always better to use the optimum operating temperature even if the drying time may be slightly prolonged.
The air must have minimum moisture levels for faster drying. We recommend the desiccant wheel for maximum dehumidification.
The right rate of airflow should be neither too fast nor slow. It should be at an optimum rate. Still increasing the air velocity may promote more mass and heat transfer. It may also improve the energy-efficient ratio, and reduce the drying time leading to less energy consumption.
When it comes to the product parameters, two things are considered:
For instance, if the initial moisture content is 30%, more time will be required compared to a material with a moisture content of only 10%.
Larger batch quantities will also need more time in the fluidized bed dryer than smaller batch quantities.
In summary, the main factors that influence the drying rate are:
The flow rate of inlet air
The amount of material loaded into the fluid bed dryer

The fluidized bed dryer produces quality granules. These granules have high porosity, and in the pharmaceutical industry this is very important for several reasons:
Porosity defines the quality of a particle being porous or having small holes. With high porosity, liquids such as water have an easy time going through the tablet matrix. Once the liquid penetrates, it dissolves and disintegrates the tablet.
Disintegration and bioavailability are thus influenced by porosity. Also, porosity influences:
Senieer offers state of the art fluid bed drying units for a wide range of applications. You’ll find every feature in our models as in similar international brand items. On-going research and development ensure we improve the fluid bed drying machines.
What’s different about Senieer is that you can get very competitive pricing. We also offer more support and better after-sales services.
We have different sizes and models for your production needs. The company can also offer turnkey solutions (custom fluidized bed dryers) since we have the factory and technical team to handle your order.
The cost of the equipment depends on the model’s production capacity along with the options you select. For instance, you can opt for the 10 Bar explosion-proof fluid bed dryer design that’s more expensive than the 2 Bar fluidized bed dryer.
For the best and lowest price, just send us a quote here.
Senieer can also offer a through-wall structure, among other custom solutions.
Check out our pharmaceutical machine videos: Senieer YouTube